THE REASON FOR CARBON FOOTPRINTING
The European Climate Agreement legally requires companies to demonstrably reduce their emissions by 55% below 1990 levels by 2030. Ultimately, emissions must be net zero. To this end a variety of regulations have been developed at the EU level, such as the CSRD. This requires companies to produce sustainability reports. As the new Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS-II) is to cap and price almost all CO2 emissions from 2027, reliable and robust reporting on CO2 will become crucial. This will prevent companies from paying for someone else’s emissions.
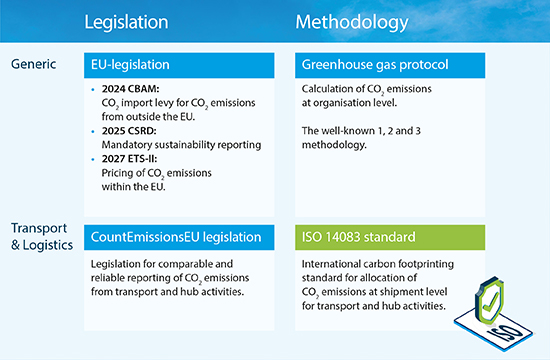
Carbon Footprinting and EU Legislation
ISO 14083 has been the international standard for Carbon Footprinting in logistics since 2023 and prescribes how companies are to allocate emissions to logistics activities. This new ISO standard harmonizes previous standards, such as EN 16258, the GLEC framework and the COFRET application guidelines.
The CountEmissionsEU legislation currently under development will require companies to use ISO 14083 to report on carbon emissions. The figure shows how European sustainability legislation and different methodologies compare.

How to work in compliance with ISO 14083
The full ISO 14083 document is very comprehensive and detailed. Here you find the key principles to follow the main points. For details, please refer to the implementation guidelines and information on ISO 14083 verification .
CPI – The most important KPI
The purpose of ISO 14083 is to assign CO2 emissions to individual shipments. For example, dividing truck trip emissions by the packages transported or dividing barge emissions by the containers transported.
The CoFRET Presentation Indicator (CPI) can do this fairly and accurately. This smart and convenient KPI forms the basis for CO2 allocation through ISO 14083. The calculation of the CPI is very similar to the calculation of cost prices in transportation: a fair share of total emissions is allocated to each shipment.
Allocating emissions through CPI
Allocation of emission through CPI takes three steps:
1 Calculate total transport performance of a trip: unit of load x bird’s-eye distance.
2 Calculate CPI: divide total kg CO2 emissions of trip by the transport performance of step 1.
3 Allocate emissions using the CPI based on transport performance per shipment.
Like to know more? On the Guidelines page at the bottom you will find detailed information about CPI.
Data quality
Reliability and accuracy of the calculation of the overall footprint depend on the data quality. Calculations based on accurately measured primary data are much more reliable than calculations based on estimates with characteristic parameters.
The recipient of the data needs to know exactly how reliable the data is. Companies that provide an indication of their own data quality and of their partners early in the chain, create clarity and unambiguity. Trendsetting companies that accurately measure and report their own data will get recognition for their efforts. Other companies will be stimulated to measure with increasing accuracy. Topsector Logistics uses four levels of data quality in Carbon Footprinting.
Learn more about using data, inferring or modeling.
Default values
For reliable emissions figures, companies depend on their own data and on data provided by subcontractors or suppliers. Sometimes these are not available. A company may be just starting to report emissions data. In such cases, reliable default data are indispensable. These must deviate as little as possible from primary measured data and give a realistic picture.
Topsector Logistics developed the Transport Performance Database with data of more than 600 logistics companies. More data are added all the time. The database provides companies sharing their information with a benchmark, allowing them to easily compare their emissions performance with others in the segment, industry or sector. In addition, companies can use the database to efficiently and accurately fill “gaps” in their own carbon accounting.

Commercial Benefits of Carbon Footprinting
Obvious benefits: Carbon Footprinting is an investment. An investment that will pay off financially. A detailed understanding of shipment level emissions shows the peaks in fuel consumption. These are the highest costs. By focusing on these improvement opportunities, you will reduce expenses as well as improve your business results.
Practical tools to implement Carbon Footprinting
Implementation of Carbon Footprinting according to ISO 14083 may seem complex, because:
- How to handle the details of allocating CO2 for your transportation mode?
- How to report correctly on the data quality of CO2 footprint?
- How to share the right information with accountants or supply chain partners?
This website provides detailed, practical information about implementing this methodology in your organization or software package. All implementation guidelines have been extensively tested and applied in logistics practice.
Want to know more?
Do you still have questions about Carbon Footprinting within transport and logistics? If so, please contact Topsector Logistiek.
T +31 15 251 65 65
M info@topsectorlogistiek.nl
Do you have a question or want to request a call back? Please leave your details.